Ophthalmic glass lens materials and manufacturing
Glass: Crown glass , barium , flint glass , titanium oxide glass, lanthanum crown glass
Glass: Crown glass , barium , flint glass , titanium oxide glass, lanthanum crown glass
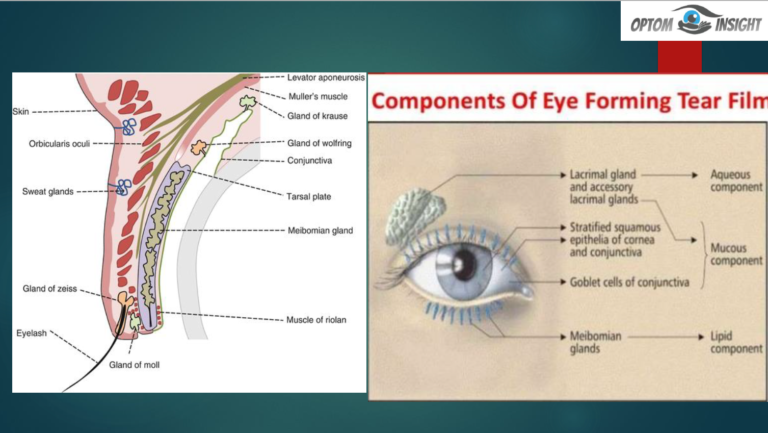
The tear film is a complex mixture of substances that are produced by various sources on the surface of the eye, such as the lacrimal gland, accessory lacrimal glands, meibomian glands, and goblet cells. This film covers the surface of…
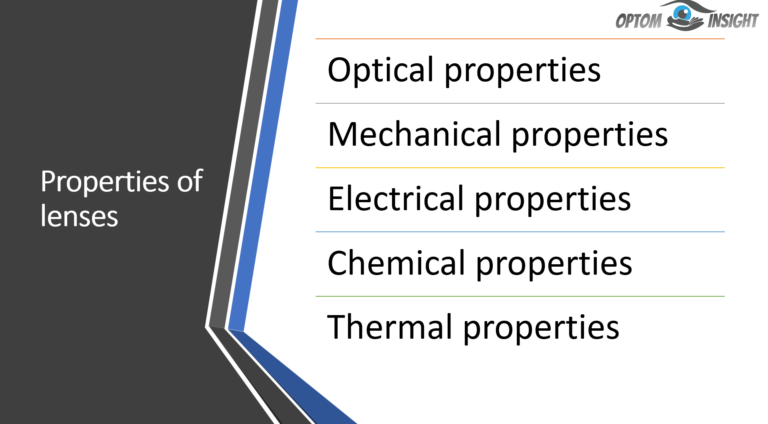
Optical properties: The optical properties of ophthalmic lenses encompass their unique characteristics that enable them to accurately refract and focus light, resulting in clear and precise vision. Mechanical properties: The mechanical properties of ophthalmic lenses encompass their physical attributes, including…
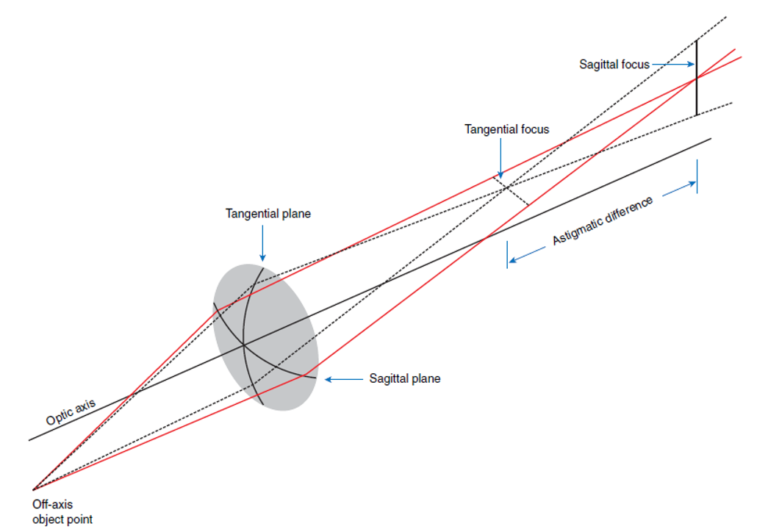
Aberration refers to the inability of a lens to create a perfect image of an object, resulting in imperfections in the formation of images within an optical system.

When a patient needs separate vision correction for both distance and near vision, they can opt for lenses that integrate these corrections into two distinct areas on each lens. Each area possesses its own focal properties tailored for specific distances.…
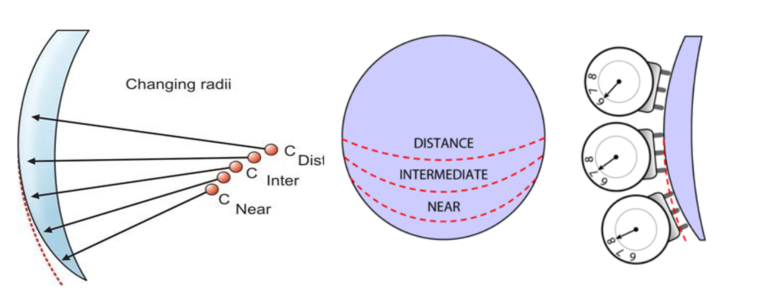
Progressive addition lenses are single-piece lenses that feature a smooth transition in curvature across the lens surface. The curvature gradually increases from the upper distance portion to the lower near portion. Unlike bifocal or trifocal lenses, progressive lenses offer a…
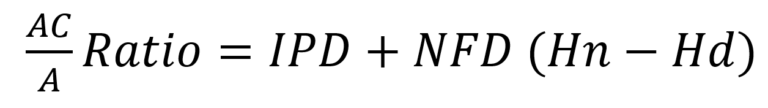
Accommodative convergence/ Accommodation ratio also known as AC/A ratio, is a measurement of changes in accommodative convergence in prism diopters induced when the patient exert or relax 1 diopter of accommodation. Changes in the accommodation are either evoked by placing…