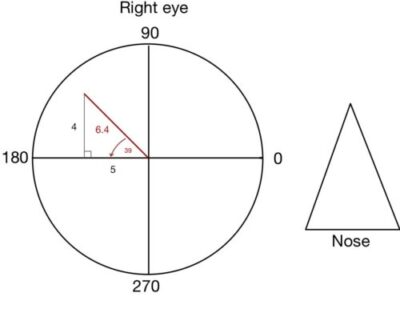
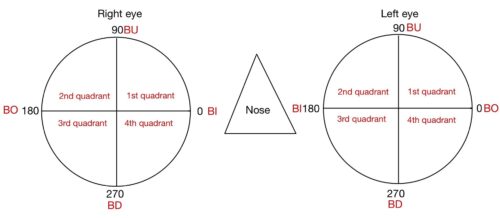
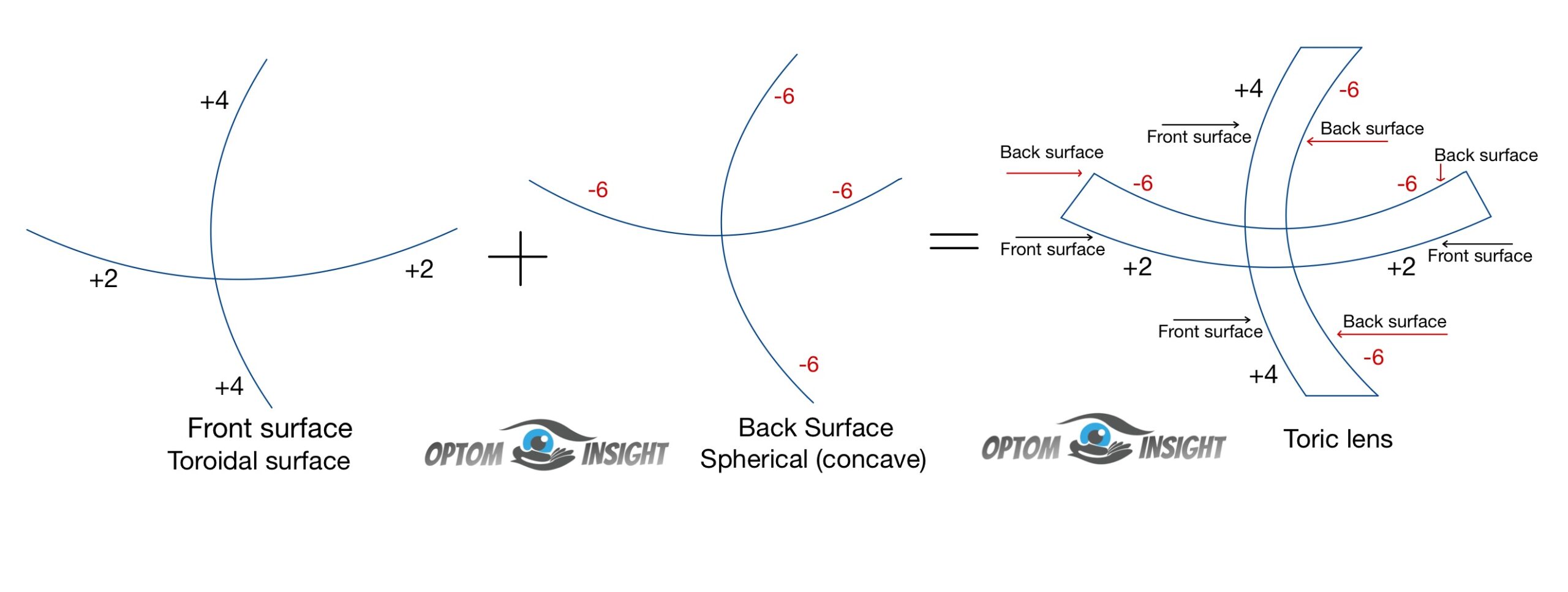
Properties of Ophthalmic lens
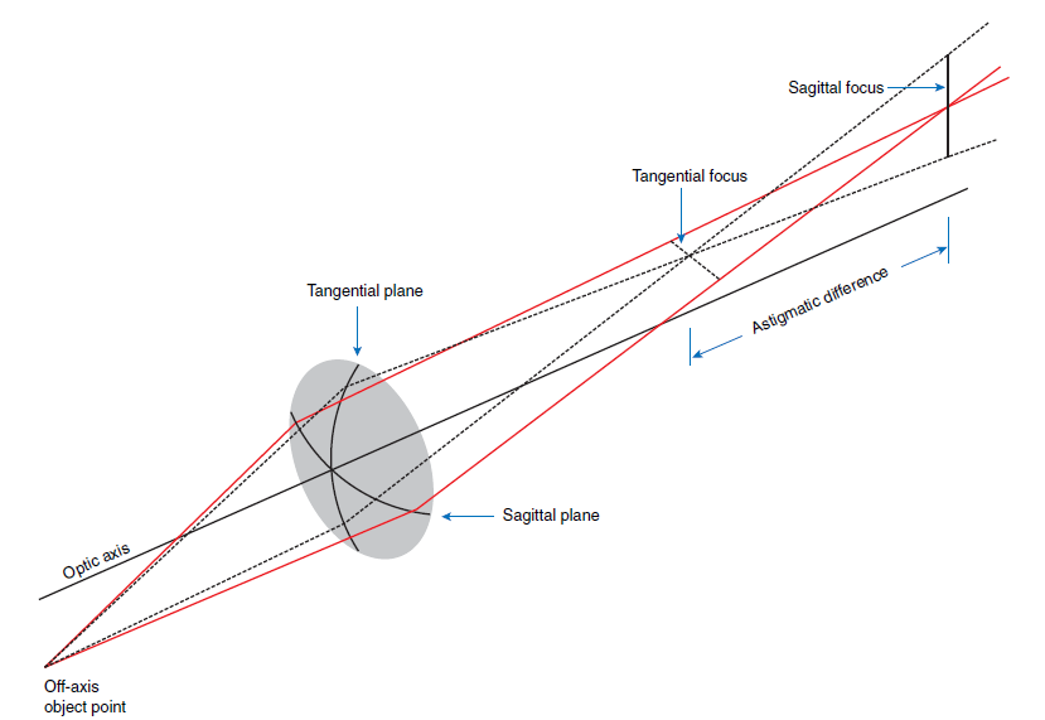
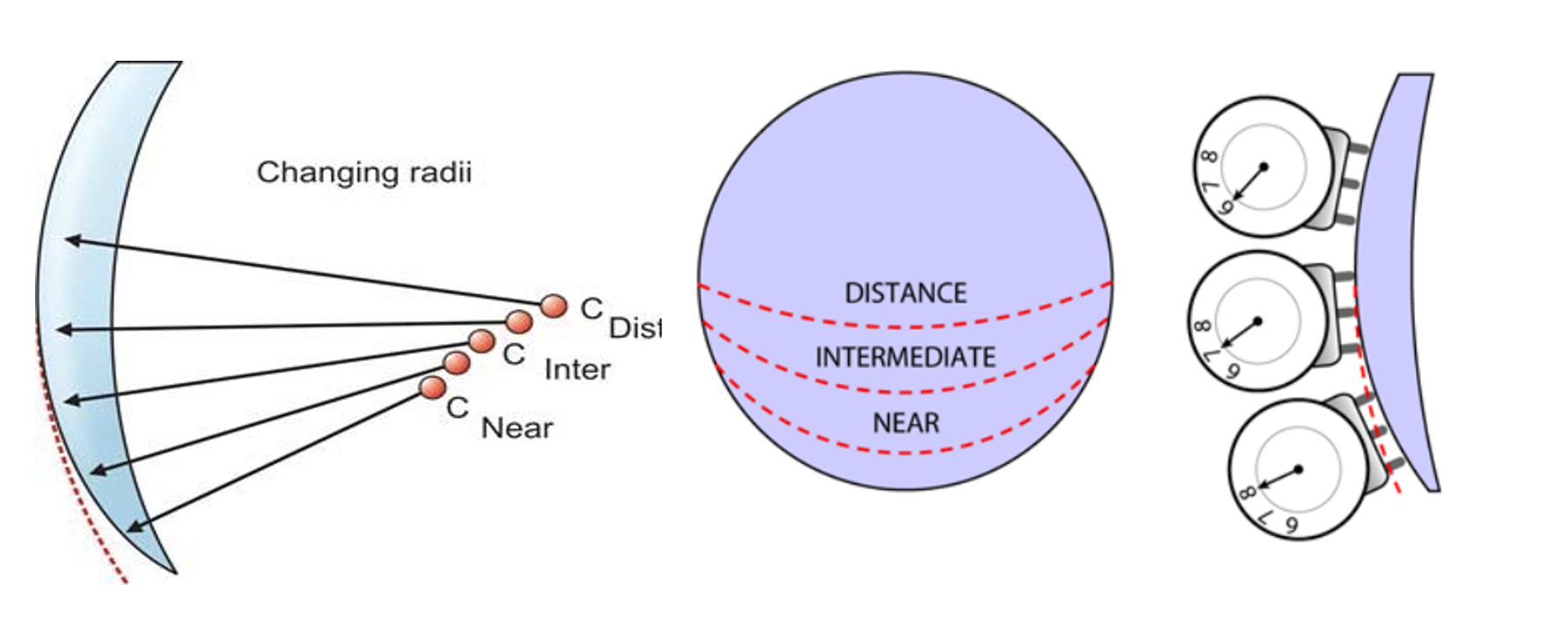
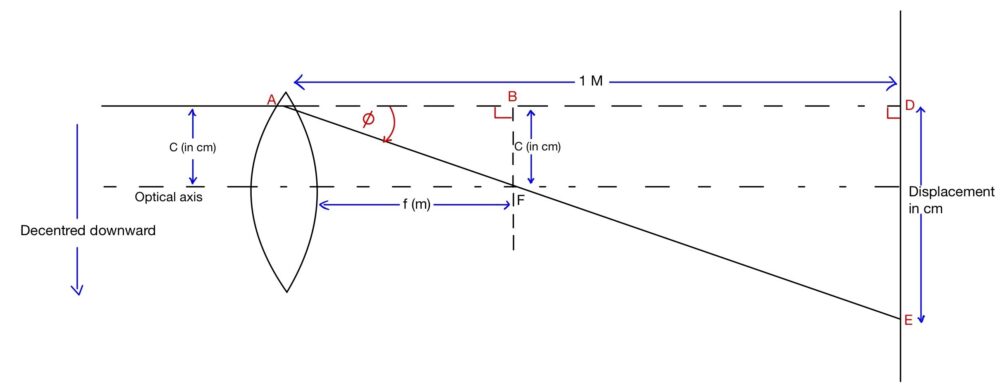
Optical properties: The optical properties of ophthalmic lenses encompass their unique characteristics that enable them to accurately refract and focus light, resulting in clear and precise vision. Mechanical properties: The mechanical properties of ophthalmic lenses encompass their physical attributes, including durability, flexibility, and resistance to impact or breakage, ensuring they can withstand everyday use and … Read more